
|
|
REGULATORY PRICING: Government control over the price charge in a market, especially by a firm with market control. Price regulation is most commonly used for public utilities characterized as natural monopolies. If allowed to maximize profit without restraint, the price charged would exceed marginal cost and production would be inefficient. However, because such firms, as public utilities, produce output that is deemed essential or critical for the public, government steps in to regulate or control the price. The two most common methods of price regulation are marginal-cost pricing and average-cost pricing.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           AVERAGE REVENUE CURVE, MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION: A curve that graphically represents the relation between average revenue received by a monopolistically competitive firm for selling its output and the quantity of output sold. Because average revenue is essentially the price of a good, the average revenue curve is also the demand curve for a monopolistically competitive firm's output. Monopolistic competition is a market structure with a large number of relatively small firms that sell similar but not identical products. Each firm is small relative to the overall size of the market such that it has some market control, but not much. In other words, it can sell a wide range of output at a narrow range of prices. This translates into a relatively elastic demand curve. If a monopolistically competitive firm wants to sell a larger quantity, then it must lower the price.The average revenue curve reflects the degree of market control held by a firm. For a perfectly competitive firm with no market control, the average revenue curve is a horizontal line. For firms with market control, such as monopolistic competition, the average revenue curve is negatively-sloped. Average Revenue Curve,
Sandwich Style | 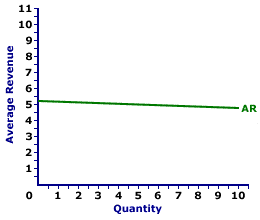 |
The average revenue curve for Manny Mustard is displayed in the exhibit to the right. Key to this curve is that Manny Mustard is a monopolistically competitive seller of sandwiches and thus faces a negatively-sloped demand curve. Larger quantities of output are only possible with lower prices.The vertical axis measures average revenue and the horizontal axis measures the quantity of output (number of sandwiches). Although quantity on this particular graph stops at 10 sandwiches, it could go higher. This curve indicates that if Manny Mustard sells 1 sandwich (at $5.20 per sandwich), then average revenue is $5.20 per sandwich. Alternatively, if he sells 10 sandwiches (at $4.75 per sandwich), then average revenue in is $4.75 per sandwich. For Manny Mustard the average revenue curve is also the demand curve. The curve is negatively sloped, meaning that larger quantities of output result in less average revenue. Although this average revenue curve, and preceding table of average revenue numbers, is based on the production activity of Manny Mustard, a well-known monopolistically competitive firm, they apply to any firm with market control. Monopoly and oligopoly firms that also face negatively-sloped demand curves generate comparable average revenues.

Recommended Citation:AVERAGE REVENUE CURVE, MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2024. [Accessed: May 2, 2024].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | |
Related Websites (Will Open in New Window)... | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
BROWN PRAGMATOX
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time flipping through mail order catalogs wanting to buy either a large, stuffed kitty cat or a cross-cut paper shredder. Be on the lookout for a thesaurus filled with typos.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
The 22.6% decline in stock prices on October 19, 1987 was larger than the infamous 12.8% decline on October 29, 1929.
|

|
|
"Leadership is based on inspiration, not domination; on cooperation, not intimidation. " -- William A. Ward
|

|
UTP
Unfair Trade Practice
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


